CATHOLICISM
The Catholic Church shares the fundamental elements common to all Christians. "Born of the Trinity", the Church is the People of God, the Body of Christ and the Temple of the Spirit. It seeks to be the sign and servant of the unity of all people with one another and with God*.
The Church was born of the Gospel, the Good News proclaimed first by Jesus and then by his Apostles. Her mission is to proclaim it to all people. Inherited from the Apostles, it is governed by their successors, the bishops, whose first and foremost is the Bishop of Rome, the Pope, the guarantor of communication between all*.
It celebrates seven sacraments: baptism and confirmation, the Eucharist, marriage, ordination, the sacraments of reconciliation and of the sick*.
Every baptised person is necessarily part of a local Church, a "diocese", of which the bishop is the pastor and enjoys great autonomy*.
The Catholic Church is therefore less "pyramidal" and more "federal" than is sometimes thought*.
On another level, just as important, faith is a lived experience, a path of life for all the baptised, each one called to holiness; it's about progressing in our relationship with God and with others. To help this spiritual life flourish, the Catholic Church offers a wealth of ways to pray (from the humble rosary to long, silent meditation) and a variety of spiritual traditions (Franciscan, Dominican, Jesuit, Carmelite, etc.)*.
A major event, the Second Vatican Council (1962-1965), is the Catholic Church's roadmap for our time*.
*Calendar of religious festivals, Alpes-Maritimes Fraternité
THE CROSS or "CRUCIFIX" recalls the Passion of Jesus and his death on the cross, but also, on the third day, his Resurrection from the dead.

Since the First Council of Constantinople, the Catholic Church has claimed a papal primacy that is not only of honour but also of jurisdiction. After the separation of the Eastern and Western Churches, the Church of Rome, known as the "Catholic Church", held a further 14 councils that laid down dogmas such as purgatory, the Immaculate Conception and papal infallibility. These councils accentuated the rupture with the Churches of the seven councils and provoked new schisms. For example, the Old Catholic Church was born out of the rejection of the dogma of papal infallibility. However, the gap between "Catholics" and "Orthodox" has been narrowing since the Second Vatican Council*.
More than half of all Christians are Catholics - 1.345 billion. Of these, 48% are American (Brazil, Mexico and the United States) and 24% European*.
*Wikipedia 2012
PROTESTANTISM
Protestantisme is one of the main branches of Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Orthodoxy. Broadly understood, Protestantism is the set of groups that "stem, directly or indirectly, from the Reformation and that reject the authority of the Pope". From this perspective, Protestantism encompasses a variety of movements ranging from Lutherans to Quakers*.
The Protestant Reformation instituted by Luther and Calvin in the early 16th century gave rise to numerous Lutheran or Reformed Protestant churches, as well as many evangelical (Baptist, Pentecostal, Charismatic Evangelical and non-denominational Christian) or liberal Christian churches*.
Protestant doctrine is based exclusively on sacred writings, i.e. the Bible, which consists solely of the Old and New Testaments. The apocryphal writings were considered by the Reformers to be interesting but not foundational to the faith, and have not been printed in Protestant Bibles since the 19th century. Protestants believe in the resurrection and eternal life (see the Gospels). Like all Christian denominations, the resurrection of Jesus Christ can be considered the essential point of the Protestant faith. The main practices are the same as those of the Catholic Church (prayers, Bible reading, Sunday worship and participation in the Eucharist, known as Holy Communion)*.
Baptism and the Lord's Supper are the only two sacraments for Protestants, who start from the principle that, according to the testimony of the biblical texts, only these two acts were instituted by Jesus Christ. In some Protestant churches, baptism is only administered as an adult, while in others the choice is left to the individual and infant baptism is widely practised*.
In 2011, these churches together accounted for around 37% of Christians, or 800 million Protestants*.
*Wikipédia 2012
The five solae of Protestantism
Sola scriptura : "Scripture alone", which we read in the Bible, which each of us is invited to hear and interpret with the inner witness of the Holy Spirit.
Sola fide : "faith alone", which is a gift from God, not just belief, but trust in God.
Sola gratia : "grace alone", which comes to meet our imperfection, our finitude, to put us back on our feet, just as we are. We do not deserve this grace through our good deeds; it is given to us.
Solus Christus : "Christ alone", with whom we are all invited to live in relationship.
Soli Deo gloria : "To God alone be glory", because to God alone goes our adoration.
*Calendrier des fêtes religieuses, Alpes-Maritimes Fraternité
The Huguenot cross
is a Protestant symbol from the south of France
From the HUGUENOTE CROSS hangs the dove, symbol of the Holy Spirit, the gift of peace on Earth made by the cross of Christ*.
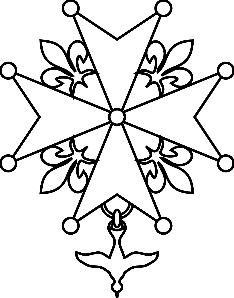
Huguenot cross with fleur-de-lys
Anglicanism is a Protestant denomination found mainly in the United Kingdom, in English-speaking countries, both in the former British colonies and in British expatriate lands around the world*.
The word « Anglicanism » was first used in the 19th century. Outside England, Anglicans are sometimes referred to as « Episcopalians », particularly in the United States and Scotland. This is because Anglicanism operates under an episcopal system, unlike other Protestant denominations, which tend to be presbyterian-synodal or congregationalist*.
The origins of this denomination can be traced back to the decision of King Henry VIII of England in the 16th century to break with the Pope, primarily for political rather than theological reasons, through the Act of Supremacy (1534)*.
Sometimes presented as a via media (middle way) between Catholicism and Protestantism, the churches of the Anglican Communion consider themselves to be in continuity with the apostolic succession and adhere to the theological principles of the Protestant Reformation, in particular the centrality of the Holy Scriptures and liturgical celebrations in the vernacular*.
Anglicanism symbols*
The Canterbury Cross is the symbol of the Anglican Use Society
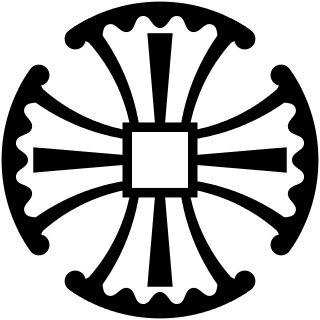
* Wikipédia 2024